Website Audit Checklist: Things to Check After Launching Your Website
Is your website design complete and ready to launch? To make it a success, it is necessary to look at different aspects that will help bring more traffic and leads to your website. We’ll cover everything in this post that will help you stand ahead of your competitors. If you are a beginner, you might come across various new terms but our guide will discuss everything in detail for better understanding.
We will make sure that you don’t miss the major points that will help bring traffic to your website organically. Let’s start with the blog.
Website Audit Checklist
1. Check for Minor Errors
Firstly, go through the whole website and take a good look at your content, menu, design, and everything. No doubt, your hired web designer would have a great job but at times they also make little errors. So, check for little issues in your content, videos, and dummy text
Make sure the content is easy to read, short, and describes your services well. Check if proper use of headings and bullet points is available in your content. Also, do not miss to check if all the images used on the website are properly optimized and labeled.
Lastly, the embedded videos are working properly. If you are linking to Embed URLs, avoid it.
2. Check the Contact Page
Having a contact page allows visitors to reach out to you or connect for the services. It adds credibility as well as improves the trust quotient. A well-designed contact page will help users to send queries and quote requirements. Make sure you have a contact page on your website that includes the form, and NAP (Name, Address, and Phone Number) details on it. In fact, if you have a Google My Business account for your business, embed your map on it.
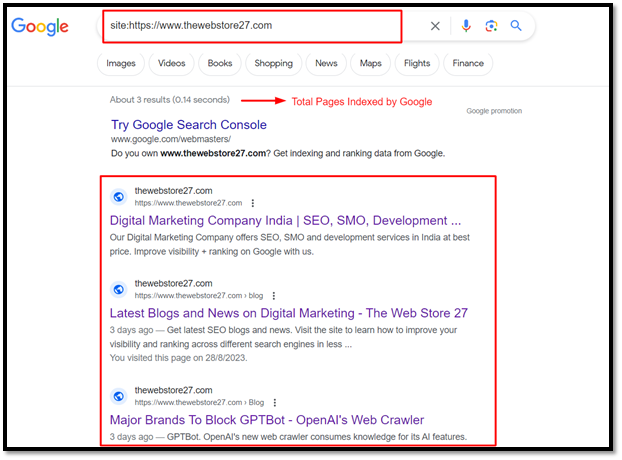
3. Is Your Site Indexed by Search Engines or Not?
To manually check if search engines like Google and Bing have indexed your site or not, go to google.com and type site:domain.com
For example, if I have to check how many pages of my site are getting indexed by Google, I will type site:https://www.thewebstore27.com/ on Google or Bing or other search engines.
4. Test Site’s Usability
Verify that the website’s functionality in all aspects operates as expected. Both conversions and overall SEO depend on usability. The most important thing is to view every component of your website through the eyes of a visitor.
– Make sure all images are well-optimized and compressed.
– Test all contact forms and call-to-action forms in particular.
– Check the login process, roles, and credentials on a multi-user website.
– Examine the entire experience as seen by a user who is perusing the website’s content.
– If you have autoresponders, check that they answer as you expected.
– If you plan to take payments through your website, test each stage of the purchase and payment process, including the success page redirect. This contains buttons, links, shopping cart features, email notifications, downloads, and sign-ups.
Ranking Factors One Must Never Ignore
5. Website Navigation
On your website, users should never be in doubt about which button to click next. Additionally, your site search ought to be accurate and seamless. Try navigating your website’s various sections like a casual visitor would.
6. Website Speed Optimization
It’s important to evaluate the performance of your site before making any modifications that may affect how it loads and manages information. You may use free tools like Page Speed Insights or GTMetrix to check your current loading time. Generally, users switch to other platforms when they find a website is taking too much time to load its content. Hence, make sure your website speed is fast and it takes less time to load all the content.
7. Check Mobile-Friendliness
Given Google’s emphasis on mobile-first indexing, testing for mobile compatibility is now a crucial step in the launch of every website. Your website must therefore be mobile-friendly and equally usable and appealing on mobile devices as it is on desktops.
To put it another way, the text should be simple to read on mobile devices, content should be consistent between versions of your website, navigation should be simple, buttons should have adequate spacing, etc.
To check if your website is mobile-friendly or not, click here.
8. Review Browser Compatibility
Sometimes there are cases in which the website opens only on your browser but not on the rest. Hence, you must always check if your website appears in different versions of top browsers. For example, Firefox, Safari, and Chrome.
You can also test your browser compatibility using the free tool – Browsershots.
To open your website in multiple browsers, it makes use of several computers located in various regions. After that, it takes screenshots of your website in several browsers and uploads them to a central, dedicated server for your evaluation.
9. Check 404s
New websites hardly have 404s errors. However, a user could make a typing error or accidentally land on a “Page Not Found” error page. Hence, make sure to have a personalized 404 page just to ensure that you don’t lose this visitor and to enhance user experience.
10. URL Status and Rewriting
All the URLs must be changed when a site is transferred from the staging area to production. Before continuing any further, make sure to confirm that all of the URLs on the live version of your site are accurate.
As per Mueller, SEO doesn’t care about the length of URLs. Exceptionally, in the one circumstance where it might. It is best to keep it around 1,000 characters, but it is merely for the sake of making monitoring simpler. Furthermore, it doesn’t matter how many slashes are present.
Canonicalization is the sole aspect of Google’s ranking algorithms where URL length may be taken into consideration.
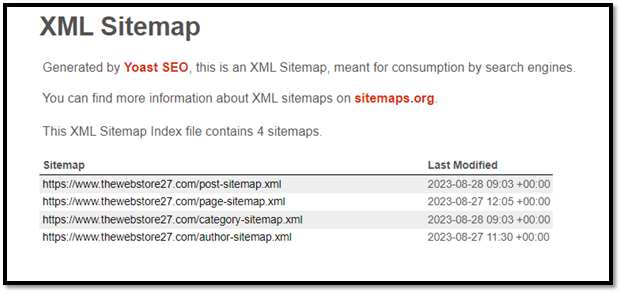
11. Check XML sitemaps/HTML sitemap
XML Sitemap is a form of blueprint of your website that makes it easier for Google or other search engines to discover all the data. Since Google indexes web PAGES rather than just websites, having an easy way for Google to find your site’s pages is crucial for SEO.
We strongly advise having an XML Sitemap because it has no drawbacks and can help your SEO.
Some websites generate XML sitemap automatically through plugins, while others prefer adding it manually.
You can check if your website has one simply by typing domain.com/sitemap.xml
For example, in my case, https://www.thewebstore27.com/sitemap_index.xml
The screenshot displays a sitemap generated via the Yoast SEO plugin.
Read More – Should You Add a Sitemap Manually or Automatically?
12. Check Google Caching Date
The caching date tells you the most recent time a search engine or web cache indexed and cached a copy of your website. You can tell if the information provided to consumers and search engines is current by looking at this date. Out-of-date material can make users unhappy and have a bad effect on SEO. So, it is important to track your cache date. But, how?
Using “cache” operator was one of the methods that most experts used to track their website’s caching date, for example, cache:yourwebsite.com
However, Google has finally retired cache links and disabled cache functionality. So, how to check one?
Well, you can use Google Cache Checker from SE Ranking.
13. Track Current Domain Authority, Page Authority, and Spam Score
Domain Authority – Domain Authority (DA), is a search engine ranking factor that determines how likely it is for a website to appear in search engine result pages (SERPs). Scores for domain authority vary from one to 100, with higher scores indicating a higher possibility of ranking.
Page Authority – How well a certain page will rank on search engine result pages (SERP) is predicted by the Page Authority (PA) score. A page’s ability to rank is determined by its Page Authority score, which ranges from one to 100.
Spam Score – The percentage of websites with features comparable to the one you’re researching that were identified to be punished or banned by Google is represented by the spam score.
-
- Low Spam Score – 1%-30%
-
- Medium Spam Score – 31%-60%
-
- High Spam Score – 61%-100%
It’s not always true that a website with a high Spam Score—whether it’s your own or one you’re visiting—is spammy. It’s a warning that you ought to look into the reliability and applicability of this website further.
It is recommended to keep note of domain authority, page authority, and spam score in the beginning before hiring an expert for site promotions and optimization. The purpose is to track how much you have improved over time. As stated above, a spam score will help you look into the reliability and applicability of your website.
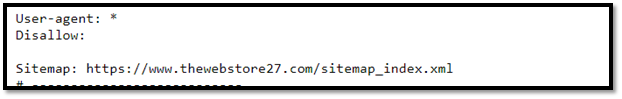
14. Robots.txt File
The URLs on your website that a search engine crawler may visit are specified in a robots.txt file. This is mostly intended to prevent your website from becoming overloaded with queries; it is not a method of keeping a website off of Google. Use noindex to prevent indexing of a page or password-protect it to prevent Google from finding it.
You can have a crawl budget issue if it’s difficult to get all of your pages indexed. By using robots.txt to blacklist irrelevant pages, Googlebot may focus more of your crawl budget on the truly important pages.
You can check if your website has one simply by typing domain.com/robots.txt
For example, in my case, https://www.thewebstore27.com/robots.txt
15. Social Media Integration
Check to determine if your social media icons are functioning properly by using them. Are they pointing to the correct pages? Have you inserted the correct buttons? If you use the “share” feature, does it operate properly?
16. Confirm your SSL
Do you know that if your website doesn’t have an SSL certificate, it could be flagged as “Not Secure” by search engines?
By certifying SSL security certificates, SSL is a well-known security standard that enables you to safeguard online transactions.
Check for the SSL certificate issued by the website you are attempting to access to quickly determine if your connection is secure.

17. Check for Canonical Issue
Similar material on different URLs can cause indexing issues, which is worse because it could reduce the value of your links and lower the search engine rankings for your website.
The most frequent reason for a canonical problem in SEO is when a website has numerous URLs that show the same or similar content. They might also happen as a result of bad redirection.
For example,
https://www.thewebstore27.com/
https://thewebstore27.com/
http://thewebstore27.com/
http://www.thewebstore27.com/
Although each of these pages is distinct, search engines recognize that there is only one page because they all utilize different URLs. Duplicate material becomes a problem as a result, which might lower SEO rankings.
In simple terms, if your website is not redirecting to a common URL or opening in different versions, you are having a canonical issue.
18. Set up Google Analytics
You may wish to monitor website traffic after launch to understand your target market. Google Analytics allows you to track:
-What devices do visitors use to access your most popular pages, blogs, and items, as well as the general profiles of your visitors
– User interaction and conversion rates
– How well marketing campaigns work
– How quickly your website loads
– The sources of traffic
..and much more information. Here’s how you can set up a Google Analytics account.
19. Set Up Google Webmaster
You can identify problems with your website using Google Search Console or Google Webmaster Tool, which can also keep you informed about whether or not your website has been compromised by malware.
Accurate information on impressions, clicks, click-through rates, and average position is provided by Google Webmaster Tools.
You submit your sitemap with Google Webmaster. Also, it allows you to send requests for indexing using the URL Inspection Tool in it.
To create a Google webmaster account, click here.
Although rather extensive, this website audit checklist is not all-inclusive.
You can save time and decrease the possibility of manual errors by using free tools to speed up the procedure. By going through each item on the checklist above, you can greatly benefit your client and create a successful website.
But for your website’s SEO optimization, you first need to understand how search engines work?
For more such updates, follow on LinkedIn.
