Website Crawling in SEO
No matter whether you have a single page website or a large website with hundreds of pages, crawling is essential in each case.
If due to some error or reason, your website or web pages are not getting crawled by search engine bots, there is a high chance that you may gain less visibility on the search results page than your competitors.
What is Crawling in SEO?
Basically, crawling is the discovery process in which search engines send their bots to the website to explore new and updated pages. The whole process of crawling can take a few days or weeks depending on your website’s optimization. For example, if your pages are properly connected and passing juice, crawlers can easily discover the content via links no matter what format you want the crawler to discover.
Googlebots visit the main webpage and then follow the link to look for new URLs and updated content.
In case, you want the crawler to discover a specific page, you can use the URL Inspection Tool in the Google Webmaster.
Note: There is a specific limit to submitting individual URLs in the URL Inspection Tool i.e. 10/day. But by using the Google Search Console URL Inspection API, you can avail the daily limit of up to 2000/day.
Another important point that you must not miss out on with the URL Inspection tool is that no matter how many times you request a recrawl of the same page, it won’t get crawled any faster. So, focus less on the amount of crawling. Instead, keep your focus on the quality of crawling.
Read More: How to Set Up Google Webmaster Account?
Now, how to measure the website crawling?
It is really important to track when the content was added/updated to the website and the time a bot took to crawl your changes. This time period between the content creation and website crawling is referred to as crawling efficacy. The best way to check this out is through your XML Sitemap. Visit your sitemap and check the last modified date and time. For the last crawling period, type cache:url and it will show you when was the last time crawlers visited that specific page or you can use the URL Inspection API.
Solution: You can use Google Search Console Manual Submissions (most common), Google Indexing API, or Index Now.
Secondly, you must calculate an indexing efficacy score. This means after creating the new content or republishing it, how much time does Google or any other search engine take to index the page?
How to Enhance Crawl and Indexing Efficacy?
XML Sitemap: First and foremost, check your XML sitemap and ensure it is properly optimized. You can add a sitemap in two forms – automated or manual. Generally, the manually added sitemap is not optimized. So, make sure your sitemap’s last modified date and time are optimized for which you can even add an automated sitemap generated via plugins like Yoast SEO or All-in-One SEO.
Internal Links: Make sure to review all your sitewide links so that the crawler can easily discover pages via links. Also, have breadcrumbs for both desktop and mobile devices. Check your SEO-relevant filters (Title Tag, Heading Tag, Canonical, URL, etc.) are crawlable. Note: Go to your phone and turn your Javascript off to check if you can easily navigate those links. If not, surely Googlebot can’t and it may impact your indexing efficacy score.
Reduce Tracking Parameters: Most marketers and businesses use different UTM tags and tracking codes to keep track of website visitors, email, and social media traffic. However, there is no reason why those tracking URLs should not be accessible to Googlebot crawlers. Instead, they can harm you if you lack proper indexing directives and bots crawl them. So, to stop bots from crawling them, use a hash to begin your string of UTM parameters rather than a question mark. Note: It’s not crawlable by Google or any other search engine, but it still tracks flawlessly in Google Analytics.
What is Crawl Budget?
Your crawl budget is the total number of URLs on your website that search engines will find and crawl within a specified amount of time. Upon exceeding your budget, the web crawler will cease accessing content from your website and proceed to other websites.
Each website can have a different crawl budget. Generally, it is automatically set by Google based on your site size, server setup, update frequency, and links.
Unlike crawling efficacy and indexing efficacy, crawl budget is not a quality indicator.
Crawl-related errors can indeed hinder Google from accessing the most important content on your site. But still, it is not a quality indicator.
Requesting Googlebot to crawl your site more often is in no way going to help in the ranking unless the information updated on the website meets the audience’s standards.
Common Issues Affecting Googlebot’s Site Access
HTTP status codes, network issues, and DNS errors can play a key role in affecting your search results. Let’s have a deeper look into the common issues that might affect Googlebot’s site access:
1. Server Issues
Let’s start with the HTTP Status code. When a client, such as a browser or a crawler, makes a request, the site’s hosting server responds with an HTTP status code in the 4xx–5xx range. Also, at times 3xx for failed redirections. In case the server is responding with a 2xx code, the content might be taken into account for indexing (doesn’t guarantee). Googlebot’s capacity to efficiently crawl a website can be hampered by a delayed server response, which can result in incomplete or unsuccessful indexing. Hence, it is essential to optimize server performance and ensure the errors are timely monitored and fixed.
2. Network Issues
Similar to 5xx server faults, Googlebot handles network timeouts, connection resets, and DNS issues. Crawling instantly slows down when there is a network fault since it indicates that the server might not be able to manage the load of requests. Google didn’t show up your content because the bot was unable to connect to the hosting server. The best solution in this case is to look for blocked Googlebot IP addresses, analyze TCP packets using tools like tcpdump and Wireshark, or connect with the hosting company to fix the issue.
3. Robots.txt Blocked
Robots.txt is one of the important files that one must check in the initial stages. Also, you must keep monitoring the file later to track which all URLs have been blocked or allowed by bots to crawl. Basically, this file updates the search engine crawlers on which URLs they can access on the website and which not. The main purpose behind this file is to prevent site overloading with excessive requests.
If your robots.txt file has blocked the crawlers from accessing your site, you might face an issue with site indexing. Hence, type your website/robots.txt to check your current status.
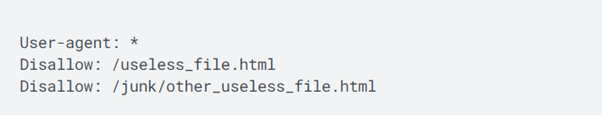
For example, in the above screenshot, you are disallowing the crawling of a single web page, i.e., useless_file.html and other_useless_file.html in the junk directory.

However, in case, your robots.txt file showed the above status, it would mean that you have disallowed crawling of the whole site.
So, look for robots.txt rules that might be another reason preventing your Googlebot from accessing the page.
It is essential that your important pages are easily crawled by bots or you might find issues in indexing. Google Search engine works in various steps, so it is essential to ensure that the pages are crawlable for the second step, i.e., indexing.
For more queries or information, feel free to contact me on my social profiles.
